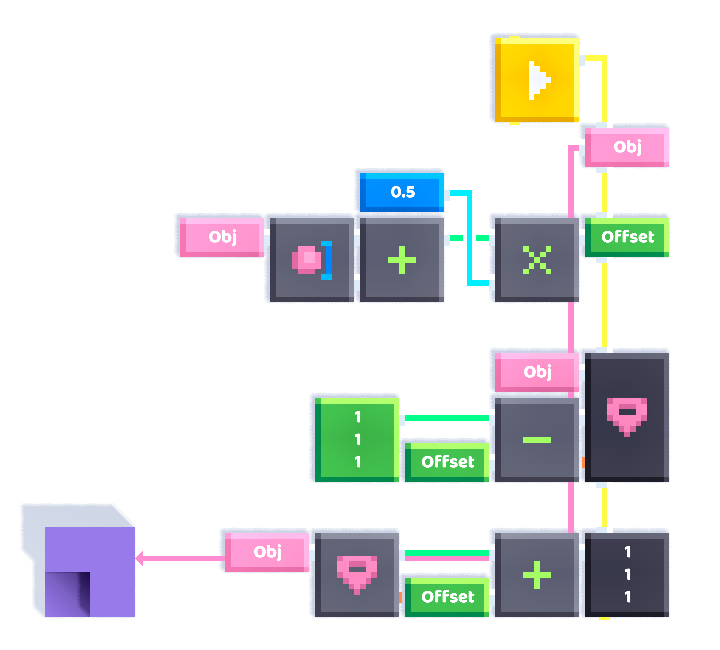
Setting the geometric position of an object
When you get the position of an object, you actually get the position of the object's centre of mass.
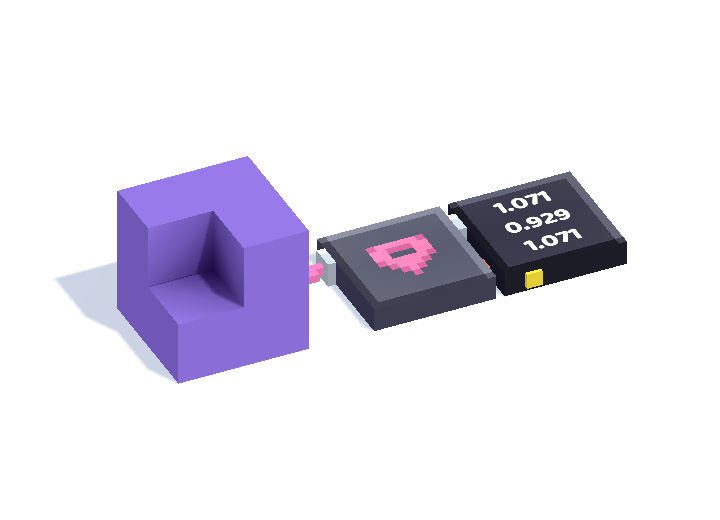
In most cases, this is enough, as the centre of mass of an object usually corresponds to its geometric centre (or centroid). However, in cases where they do not align, and you wish to get the geometric centre, getting its position will thus not suffice.
The centre of mass of an object is not the same as it's geometric position. The geometric position of an object is the midpoint of the vector between it's minimum and maximum vectors, and is the actual center of an object, which doesn't always correspond to the centre of mass of the object.
The trick is to take the Get Position vector and offset it by half the total size of the object. The "total size" of the object refers to the sum of the minimum and maximum vectors of the object.
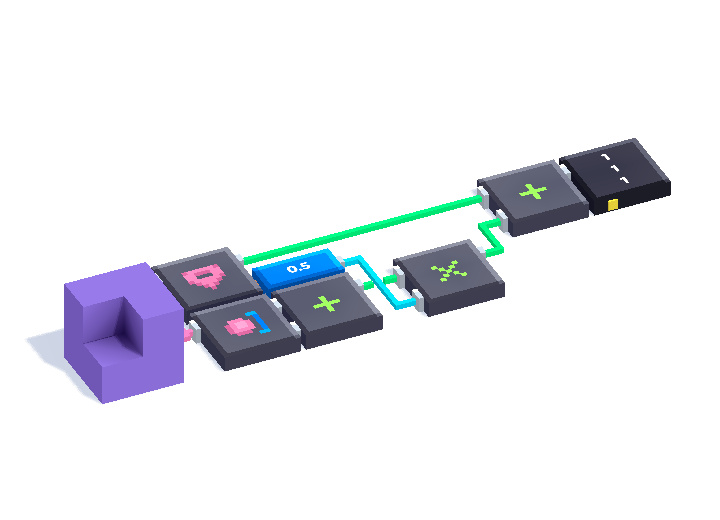
By extension, to set the geometric position of the object, set the position (centre of mass) of the object to the desired position (centroid) subtracted by the offset.